| 1 |
If not already selected, in the Surface Type drop-down list select
Fit cloud of points.
|
| 2 |
In the Input Mode drop-down list, select the method to be used:
| Select |
To create a surface by fitting a set of point entities existing in the model.
When this mode is selected, first of all you will have to select the point entities (by clicking or by using a selection operator). Once the points are selected, the
Fitting Mode must also be specified, by choosing one of the following:
|
| Import points from ASCII file |
To create a surface by fitting a set of point entities contained in ASCII file (extension ".pt"; each line in the file must contain the three world coordinates of a point; each coordinate is separated by the following through a blank character). The coordinates will be read according to the Units of measurement that you can set.
Once the file containing the point has been loaded, the
Fitting Mode must also be specified, by choosing one of the methods described for the
Select mode. |
| Fit surface |
To create a surface by fitting an existing surface to be selected.
See "Creating a Point Cloud surface by fitting an existing surface" for details. |
| Points from curves |
To create a surface by fitting the points lying on some curves to be selected. You can also define the No. of points per curve to be fitted.
|
|
| 3 |
Under NURBS parameters, you can set the values for the resulting surface. The values you can actually define depend on your former choices. The whole set is the following:
| Deg. U |
Degree of the surface along the U parametric direction. |
| Cont. U |
Continuity value of the surface along the U parametric direction. |
| Deg. V |
Degree of the surface along the V parametric direction. |
| Cont. V |
Continuity value of the surface along the v parametric direction. |
| Arcs U |
Number of arcs of the surface along the U parametric direction. |
| Arcs V |
Number of arcs of the surface along the V parametric direction. |
|
| 4 |
Once you have completed the necessary selections and set the parameters as you like, you can click the Preview button (  ). The preview of the resulting surface will be displayed. ). The preview of the resulting surface will be displayed.
The fitting parameters will also be displayed:
- Max. distance
the distance of the point that is farthest away from the fitting surface, which you can display by selecting the Most distant point check box.
- Mean square error
Let di be the distance of the point Pi from the fitting surface and n the number of points to be fitted. The mean square error Eqmis the following:
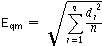
You can iterate the fitting process by clicking Mean square error, thus reducing the above said values. The number of iterations can also be set (in the
No. of iterations box).
Finally, You can have a preview of the control points for the resulting surface by checking the Show Control Points box.
|
| 5 |
Click  or or  to confirm your selections and create the surface, or click to confirm your selections and create the surface, or click  to discard your changes. to discard your changes. |
 Fit cloud of points option of the
Point Cloud command enables you to create a surface by fitting a given set of points or an existing surface.
Fit cloud of points option of the
Point Cloud command enables you to create a surface by fitting a given set of points or an existing surface.
 ). The preview of the resulting surface will be displayed.
). The preview of the resulting surface will be displayed.
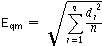
 or
or  to confirm your selections and create the surface, or click
to confirm your selections and create the surface, or click  to discard your changes.
to discard your changes.