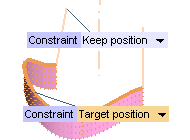
The Rotational Sweep command enables you to perform GSM based transformations (Scaling set to GSM) while maintaining additional tangency constraints. For example, a section with a tangent perpendicular to the axis will be swept in such a way that it remains perpendicular throughout the sweep. Two Constraint drop-down lists (mini-dialog box) have been introduced, which are displayed over the section curve and drive curve, respectively.

The Constraint drop-down list for the section curve has the following options:
| Keep position | Sweep surface boundary is unchanged. |
| Keep position + tangent | Sweep surface boundary is unchanged and also its tangency field is preserved. |
The Constraint drop-down list for the drive curve has the following options:
| Target position | Sweep surface is transformed to match the drive. |
| Target position + keep tangent | Sweep surface is transformed to match the drive and also its tangency field is preserved. |
| Target position + target tangent | This option is available only if the drive curve is a surface boundary. Sweep surface is transformed to match the drive and ensure tangent continuity with the boundary surface along the drive. |
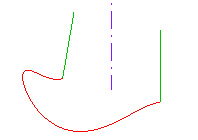
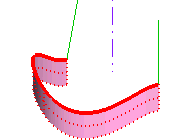
Consider the following example in which:
|
|
 |
 |
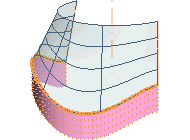
Some rotational sweep results obtained by using the various constraints are shown below. The red arrow highlights where the tangency constraint is applied.
 |
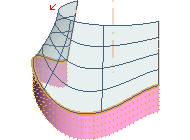 |
|
|
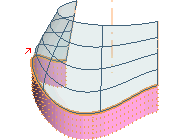 |
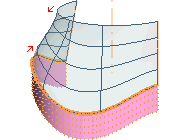 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
|