Please note that you can accomplish this task by loading file "spf_constant.e3".
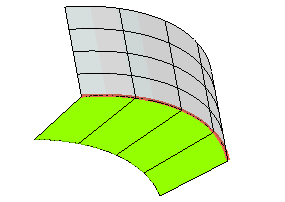
In this task you will use the Spined Fillet command to create a fillet between two surfaces along a spine curve. The radius of the fillet will vary between an in initial and a final value, and you will also specify some points where it must assume values of your own choice.
Please note that you can accomplish this task by loading file "spf_constant.e3".

| 1 | Start the Spined Fillet command. |
| 2 | In the Type drop-down list select
Variable radius. |
| 3 | Select the first surface (Group A).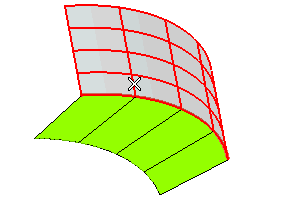 Right-click and select Continue to end selection for the first group of surfaces. |
| 4 | Select the second surface (Group B).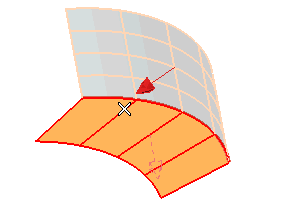 Right-click and select Continue to end selection for the second group of surfaces. |
| 5 | As you can see, the normal of the second surface is outward bound. If you keep it like that, you won't be able to create the fillet, as the normal of the first surface is inward bound instead. To invert the direction of the normal, thus enabling the creation of the fillet, double-click on the arrow representing the normal of the second surface.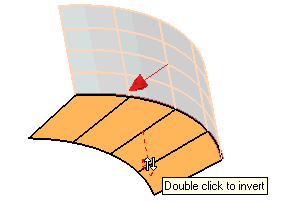 |
| 6 | Select the spine curve.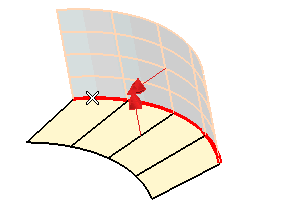 |
| 7 | In the Start Radiusand
End Radius mini-dialog box respectively, type the initial and final value of the radius of the fillet you want to create.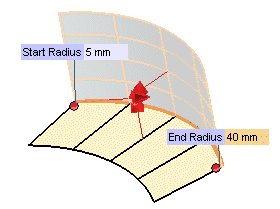 |
| 8 | To specify additional intermediate values fro the radius of the fillet, first click Internal Points in the selection list and then click at as many locations along the spine curve as you like. In the corresponding
Radius mini-dialog box, type the value of the radius for that location. The internal points can also be specified using the snap commands. Furthermore, it is not necessary to indicate them exactly on the spine chain: wherever you specify them, they will be projected onto it.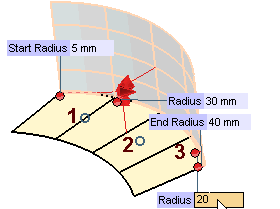 |
| 9 | Set Extension drop-down list to
Disabled and then click  or or  to confirm your selections and create the fillet: to confirm your selections and create the fillet: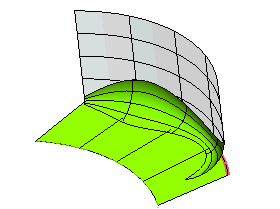 |