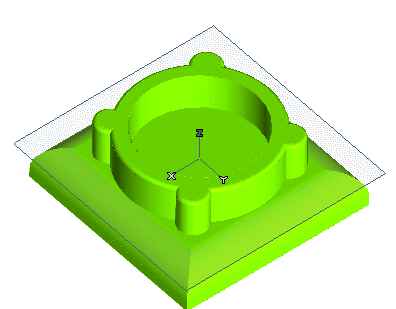
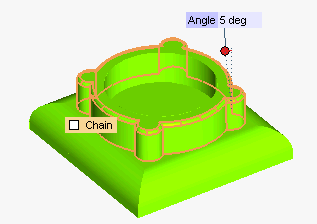
Start the Zone Draft command. You will add a draft angle about the Z axis to the side faces of the upper protrusion.
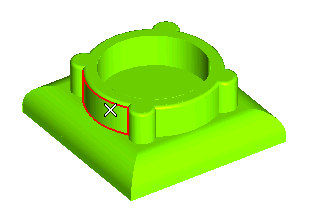
The Chain check box shows up, as the currently selected faces have tangency continuity with others faces in the same solid
- When the check box is not selected selection includes only the actually selected faces.
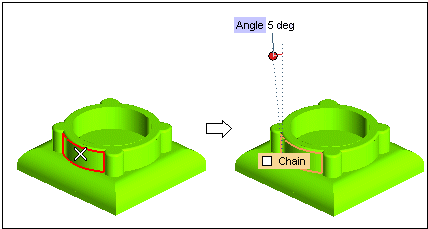
- When the check box is selected, selection includes all the faces having tangency continuity with the actually selected ones.
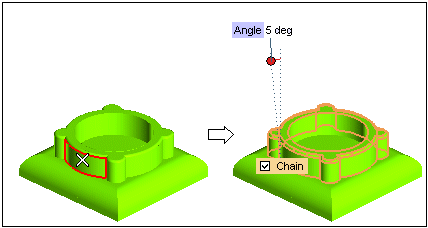
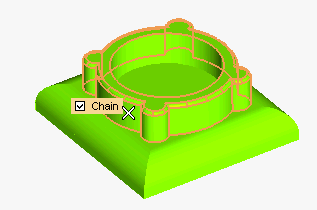
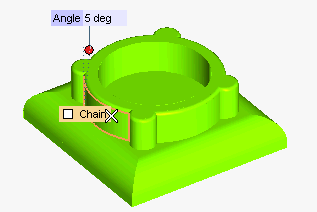
The draft angle must not be applied to the top face, so:
- Uncheck the Chain box
- Press the CTRL key and contemporarily click on the top face to deselect it.
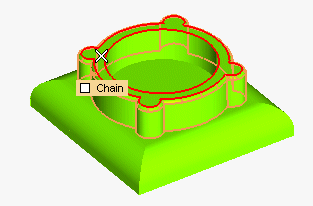
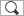
The top face has been deselected. All the faces the draft angle must be applied to are now selected (and no others).
| Choosing the drafting method The Draft constraint drop-down list enables you to choose two different drafting methods:
|
 ) to display a preview of the result.
) to display a preview of the result.
To check the precision values you obtained, you can click the Show Warnings button (
 ). You can check the results you obtained as described in "Checking your results".
). You can check the results you obtained as described in "Checking your results". or
or  to confirm your selections and modify the shape of the object.
to confirm your selections and modify the shape of the object.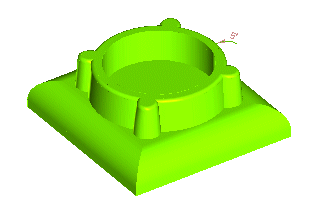
Click
 to discard your changes.
to discard your changes.While you are using the command, you can select the Hide check box to temporarily hide the original entities, in order to better appreciate the changes you are making. The entities will be hidden only as long as the command is being executed.