- Wheel-asy: The Wheel (pink in color) is mounted on its Stand (brown in color). The Wheel is free to rotate on the mounting.
- Slider-asy: The Slider (blue in color) is mounted on its Stand (brown in color). The Slider is free to slide along the guide way.
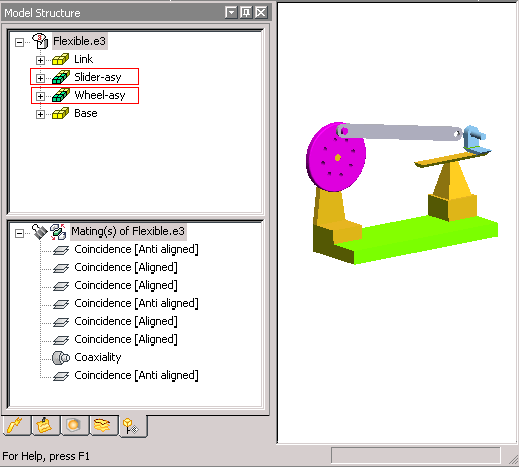
A Coaxiality constraint is already applied between the hole in the Link Rod (gray in color) and the pin on the Wheel.
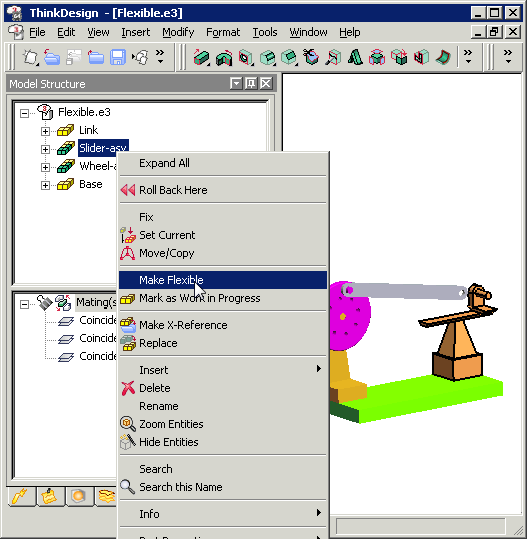 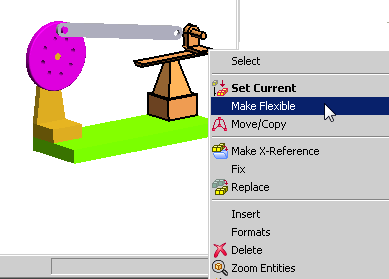 |