



 Compensator
Compensator Compute Distances
Compute Distances
The Compute Distances command is an effective tool to compute the distances between points and a shape. In fact, it provides the distances of a specified set of points from a selected shape based on a chosen projection law and also provides information about the maximum, minimum and mean distances. After starting the command, you can use the following selection list options to proceed.
| ASCII file | To read the points in an ASCII ".pt" file, in which each line contains the coordinates of one point in the World Reference system (the coordinate separator is a blank character). In this case, the Browse option will be displayed in the selection list. By selecting it, a file selection box will be displayed enabling you to select the required point file. The unit of measure for the point coordinates can also be selected in the Unit of Measurement drop-down list. |
| Standalone | To select the points (by using the Points selector) directly in the model through a window selection (or even one by one). |
| Normal | The points will be projected orthogonally onto the shape. |
| Flat surface | The point will be projected using a linear projection along a specified direction (using the Direction drop-down list). |
| Double curvature | The points will be projected using a spherical projection for which you will have to specify the center. |
| Single curvature | The points will be projected using a cylindrical projection for which you will have to specify the axis (using the Direction drop-down list). |
Once the distances have been computed, the markers displayed on the points in the model and the graphs — see "Displaying graphs in Compensator" for details on how to obtain graphs in Compensator — are separated into three differently colored zones:
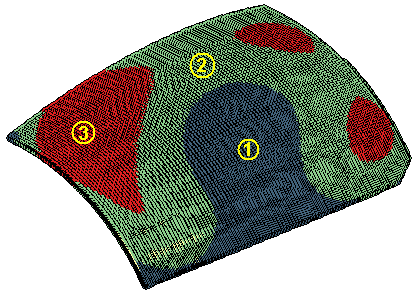 |
1 : Minimum distances - low threshold |
| 2 : Low threshold - high threshold | |
| 3 : High threshold - maximum distances |
The default values for low and high threshold are used in the computation, but you can change them to better focus on a particular range.
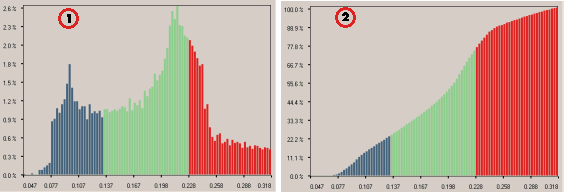
1 - Distribution 2 - Repartition