 or
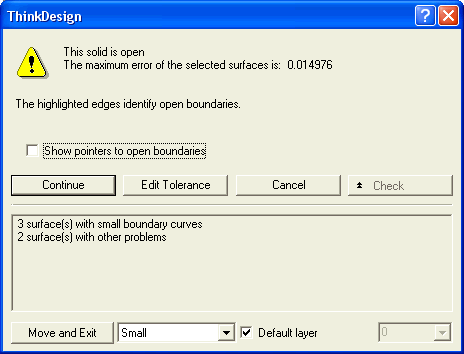
or  to confirm your selections and create the solid. As our model is not closed, the following warning is displayed.
to confirm your selections and create the solid. As our model is not closed, the following warning is displayed.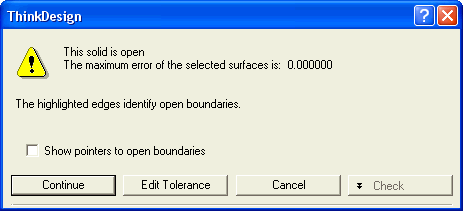
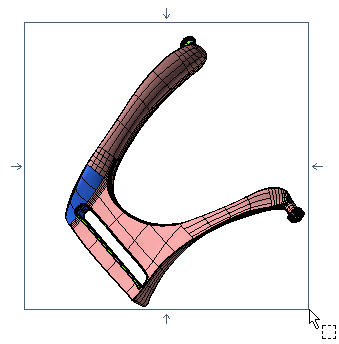
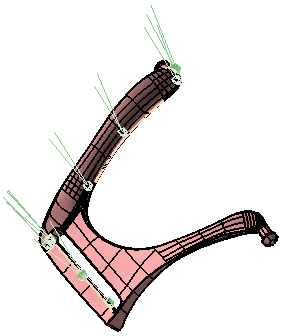
If you select Continue, an open solid will be created. On selecting the Show pointers to open boundaries check box, the open boundaries will be highlighted in the model as shown in the figure below.
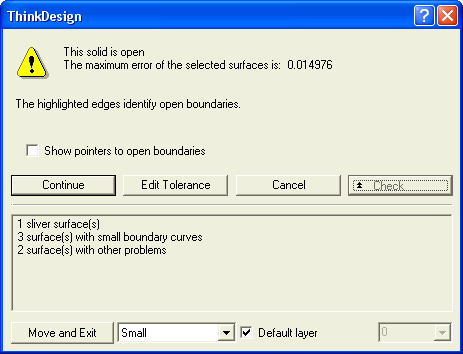
You can isolate the wrong entities by moving them to a different layer and then turning the layer OFF. To do so, select the type of issue in the drop-down list besides the Move and Exit button. The entities causing the specified issue will be moved to the layer specified by the Default layer check box and its drop-down list.
- When the Default layer check box is selected, the wrong entities will be moved to a new layer with a default name (for example "AutoLayer_ MakeSolid_Small", where AutoLayer_ MakeSolid_ is prefixed to the nature of the error).
- When this check box is cleared, the edit box and drop-down list are enabled. You can either select an existing layer from the drop-down list or enter the name of a new layer in the edit box to move the wrong entities onto it.
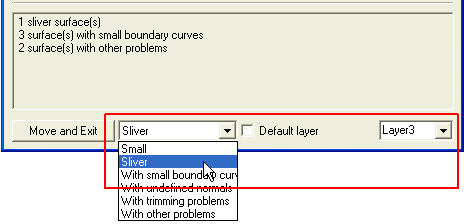
Click Move and Exit to move the surface with Sliver problem to Layer 3.
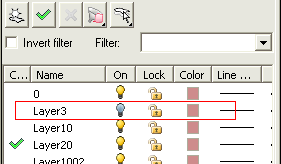
Repeat the steps from 5 and 6 so that you can the isolate the surface with other problems and solve them separately to make a closed solid.
Problems and when they occur
|