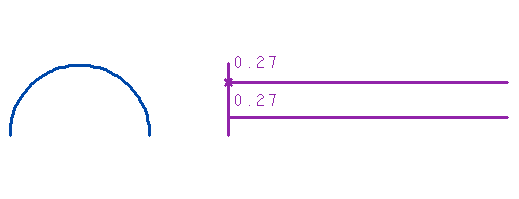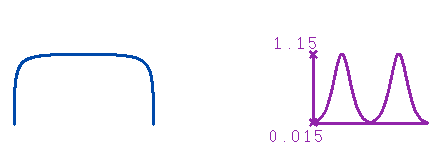Curvature analysis
The curvature value is the reciprocal of the radius.
If the radius is constant, the curvature is constant too. In the following picture you can see the
constant graph of curvature of an arc:
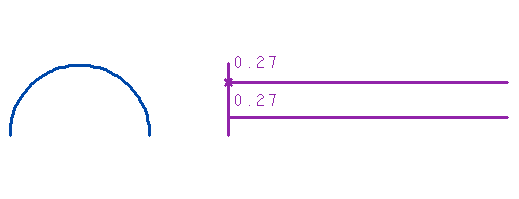
So, in the example of the picture above, the radius is r=1/0.27=3.7.
In the example of the following picture:
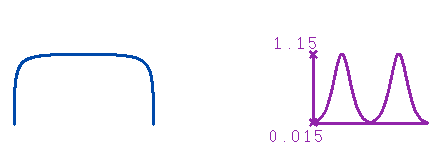
the curve on the left is obtained by an arc by modifying the weight of two of its control points.
The graph of curvature shows a regular curvature:
- if the curvature value is close to zero, this means that part of the curve has such a big radius that it's
nearly as straight as a line
- on the contrary, if the curvature value is close to 1, this means that the radius in that part
of the curve is very small (the curve is extremely "incurved").